Drone Bee (32-image Macro Stack) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A drone is a male bee. Unlike the female
 Drones carry only one type of
Drones carry only one type of
 Mating occurs in flight, which accounts for drones needing better vision, which is provided by their large eyes. Should a drone succeed in mating, the first thing that happens is all of the blood in the drone's body rushes to his endophallus, which causes him to lose control over his entire body. His body falls away, leaving a portion of his endophallus attached to the queen which helps guide the next drone in the queen.
Honey bee queen breeders may breed drones to be used for instrumental insemination or open mating. A queen
Mating occurs in flight, which accounts for drones needing better vision, which is provided by their large eyes. Should a drone succeed in mating, the first thing that happens is all of the blood in the drone's body rushes to his endophallus, which causes him to lose control over his entire body. His body falls away, leaving a portion of his endophallus attached to the queen which helps guide the next drone in the queen.
Honey bee queen breeders may breed drones to be used for instrumental insemination or open mating. A queen
 ''
''
Close-up Video of a Drone bee
Video of drones being expelled from a hive
Drone
{{DEFAULTSORT:Drone (Bee) Beekeeping Insect reproduction Bees
worker bee
A worker bee is any female bee that lacks the reproductive capacity of the colony's queen bee and carries out the majority of tasks needed for the functioning of the hive. While worker bees are present in all eusocial bee species, the term is rar ...
, a drone has no stinger
A stinger (or sting) is a sharp organ found in various animals (typically insects and other arthropods) capable of injecting venom, usually by piercing the epidermis of another animal.
An insect sting is complicated by its introduction of ve ...
. He does not gather nectar
Nectar is a viscous, sugar-rich liquid produced by Plant, plants in glands called nectaries, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollination, pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to an ...
or pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
and cannot feed without assistance from worker bees. His only role is to mate with a maiden queen
Queen most commonly refers to:
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a kingdom
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen (band), a British rock band
Queen or QUEEN may also refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Q ...
in nuptial flight
Nuptial flight is an important phase in the reproduction of most ant, termite, and some bee species. It is also observed in some fly species, such as '' Rhamphomyia longicauda''.
During the flight, virgin queens mate with males and then land ...
.
Genetics
allele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule.
Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), ...
at each chromosomal position, because they are haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the num ...
(containing only one set of chromosomes
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most importa ...
from the mother). During the development of eggs within a queen
Queen most commonly refers to:
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a kingdom
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen (band), a British rock band
Queen or QUEEN may also refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Q ...
, a diploid cell with 32 chromosomes divides to generate haploid cells called gametes
A gamete ( ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. The name gamete was introduced by the Ge ...
with 16 chromosomes. The result is a haploid egg, with chromosomes having a new combination of alleles at the various loci. This process is called arrhenotokous parthenogenesis or simply arrhenotoky
Arrhenotoky (from Greek ἄρρην ''árrhēn'' "male" and τόκος ''tókos'' "birth"), also known as arrhenotokous parthenogenesis, is a form of parthenogenesis in which unfertilized eggs develop into males. In most cases, parthenogenesis pro ...
.
Because the male bee technically has only a mother, and no father, their genealogical tree is unusual. The first generation has one member (the male). One generation back also has one member (the mother). Two generations back are two members (the mother and father of the mother). Three generations back are three members. Four back are five members. This sequence – 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, and so on – is the Fibonacci sequence
In mathematics, the Fibonacci sequence is a Integer sequence, sequence in which each element is the sum of the two elements that precede it. Numbers that are part of the Fibonacci sequence are known as Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted . Many w ...
.
Much debate and controversy exists in scientific literature about the dynamics and apparent benefit of the combined forms of reproduction in honey bees and other social insects, known as the haplodiploid
Haplodiploidy is a sex-determination system in which males develop from unfertilized eggs and are haploid, and females develop from fertilized eggs and are diploid. Haplodiploidy is sometimes called arrhenotoky.
Haplodiploidy determines the se ...
sex-determination system
A sex-determination system is a biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism. Most organisms that create their offspring using sexual reproduction have two common sexes, males and females, and in ...
. The drones have two reproductive functions: each drone grows from the queen's unfertilized haploid egg and produces some 10 million male sperm cells
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; : spermatozoa; ) is a motile sperm cell produced by male animals relying on internal fertilization. A spermatozoon is a moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete that joins with an ov ...
, each genetically identical to the egg. Drones also serve as a vehicle to mate with a new queen to fertilize her eggs. Female worker bee
A worker bee is any female bee that lacks the reproductive capacity of the colony's queen bee and carries out the majority of tasks needed for the functioning of the hive. While worker bees are present in all eusocial bee species, the term is rar ...
s develop from fertilized eggs and are diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
in origin, which means that the sperm from a father provides a second set of 16 chromosomes for a total of 32: one set from each parent. Since all the sperm cells produced by a particular drone are genetically identical, full sisters are more closely related than full sisters of other animals where the sperm is not genetically identical.
A laying worker bee
A laying worker bee is a worker bee that lays fertilization, unfertilized eggs, usually in the absence of a queen bee. Only Drone (bee), drones develop from the egg (biology), eggs of laying worker bees (with some exceptions, see thelytoky). A bee ...
exclusively produces totally unfertilized eggs, which develop into drones. As an exception to this rule, laying worker bees in some subspecies of honey bees may also produce diploid (and therefore female) fertile offspring in a process called thelytoky
Thelytoky (from the Ancient Greek, Greek θῆλυς ''thēlys'' "female" and τόκος ''tókos'' "birth") is a type of parthenogenesis and is the absence of mating and subsequent production of all female diploid offspring as for example in aph ...
, in which the second set of chromosomes comes not from sperm, but from one of the three polar bodies
A polar body is a small haploid cell that is formed at the same time as an egg cell during oogenesis, but generally does not have the ability to be fertilized. It is named from its polar position in the egg.
When certain diploid cells in animal ...
during anaphase II of meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
.
In honey bees, the genetics of offspring can best be controlled by artificially inseminating (referred to in beekeeping as "instrumental insemination") a queen with drones collected from a single hive, where the drones' mother is known. In the natural mating process, a queen mates with multiple drones, which may not come from the same hive. Therefore, batches of female offspring have fathers of a completely different genetic origin.
Anatomy
A drone is characterized by eyes that are twice the size of those of worker bees and queens, and a body size greater than that of worker bees, though usually smaller than thequeen bee
A queen bee is typically an adult, mated female ( gyne) that lives in a colony or hive of honey bees. With fully developed reproductive organs, the queen is usually the mother of most, if not all, of the bees in the beehive. Queens are develope ...
. His abdomen is stouter than the abdomen of workers or queen. Although heavy bodied, the drone must be able to fly fast enough to accompany the queen in flight. The average flight time for a drone is about 20 minutes.
An ''Apis cerana
''Apis cerana'', the eastern honey bee, Asiatic honey bee or Asian honey bee, is a species of honey bee native to South, Southeast and East Asia. This species is the sister species of '' Apis koschevnikovi'' and both are in the same subgenus as ...
'' colony has about 200 drones during high summer peak time.
Drones depend on worker bees to feed them.
Drones die off or are ejected from the hive by the worker bees, which can include the workers clipping the drones' wings, in late autumn, dying from exposure and the inability to protect or feed themselves, and do not reappear in the bee hive until late spring. The worker bees evict them as the drones would deplete the hive's resources too quickly if they were allowed to stay.
Role
The drones' main function is to be ready to fertilize a receptive queen. Drones in a hive do not usually mate with avirgin queen
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudor. Her eventful reign, and its effect on history ...
of the same hive because the queen flies further to a drone congregation area than the drones do. Mating generally takes place in or near drone congregation areas. How these areas are selected is not understood, but they do exist. When a drone mates with a queen of the same hive, the resultant queen will have a spotty brood pattern (numerous empty cells on a brood frame
Brood may refer to:
Nature
* Brood, a collective term for offspring
* Brooding, the incubation of bird eggs by their parents
* Bee brood, the young of a beehive
* Individual broods of North American periodical cicadas:
** Brood X, the largest br ...
) due to the removal of diploid drone larvae by nurse bees (i.e., a fertilized egg with two identical sex genes will develop into a drone instead of a worker). The worker bees remove the inbred brood and consume it to recycle the protein.
 Mating occurs in flight, which accounts for drones needing better vision, which is provided by their large eyes. Should a drone succeed in mating, the first thing that happens is all of the blood in the drone's body rushes to his endophallus, which causes him to lose control over his entire body. His body falls away, leaving a portion of his endophallus attached to the queen which helps guide the next drone in the queen.
Honey bee queen breeders may breed drones to be used for instrumental insemination or open mating. A queen
Mating occurs in flight, which accounts for drones needing better vision, which is provided by their large eyes. Should a drone succeed in mating, the first thing that happens is all of the blood in the drone's body rushes to his endophallus, which causes him to lose control over his entire body. His body falls away, leaving a portion of his endophallus attached to the queen which helps guide the next drone in the queen.
Honey bee queen breeders may breed drones to be used for instrumental insemination or open mating. A queen mating yard A mating yard is a term for an apiary which consists primarily of queen mating nucs and hives which raise drones. A queen bee must mate in order to lay fertilized eggs, which develop into workers and other queens, which are both female. Queens can ...
must have many drones to be successful.
In areas with severe winters, all drones are driven out of the hive in the autumn. A colony begins to rear drones in spring and drone population reaches its peak coinciding with the swarm season in late spring and early summer. The life expectancy of a drone is about 90 days.
Although the drone is highly specialized to perform one function, mating and continuing the propagation of the hive, they may have other purposes. All bees, when they sense the hive's temperature deviating from proper limits, either generate heat by shivering, or exhaust heat by moving air with their wings—behaviours which drones share with worker bees.
Behavior
Drones do not exhibit typical worker bee behaviors such as nectar and pollen gathering, nursing, or hive construction. While drones are unable to sting, if picked up, they may swing their tails in an attempt to frighten the disturber. In some species, drones buzz around intruders in an attempt to disorient them if the nest is disturbed. Drones fly in abundance in the early afternoon and are known to congregate in drone congregation areas a good distance away from the hive.Mating and the drone reproductive organ
The drone endophallus is optimized to disperse a large quantity of seminal fluid and spermatozoa with great speed and force. The endophallus is held internally in the drone. During mating, the organ is everted (turned inside out), into the queen. The eversion of the endophallus is achieved by contracting abdominal muscles, which increases hemolymph pressure, effectively "inflating" the endophallus. Cornua claspers at the base of the endophallus help to grip the queen. Mating between a single drone and the queen lasts less than 5 seconds, and it is often completed within 1–2 seconds. Mating occurs mid-flight, and above ground. Since the queen mates with 5–19 drones, and drones die after mating, each drone must make the most of his single shot. The drone makes first contact from above the queen, his thorax above her abdomen, straddling her. He then grasps her with all six legs, and everts the endophallus into her opened sting chamber. If the queen's sting chamber is not fully opened, mating is unsuccessful, so some males that mount the queen do not transfer semen. Once the endophallus has been everted, the drone is paralyzed, flipping backwards as he ejaculates. The process of ejaculation is explosive—semen is blasted through the queen's sting chamber and into the oviduct. The process is sometimes audible to the human ear, akin to a "popping" sound. The ejaculation is so powerful that it ruptures the endophallus, disconnecting the drone from the queen. The bulb of the endophallus is broken off inside of the queen during mating—so drones mate only once, and die shortly after. The leftover endophallus remaining in the queen's oviduct is referred to as the "mating sign". The plug will not prevent the next drone from mating with the same queen, but may prevent semen from flowing out of the oviduct.Drone congregation areas
Mating between the drones and a virgin queen takes place away from the colony, in mid-air mating sites. These mating sites, called "congregation areas", are specific locations, where drones wait for the arrival of virgin queens. A congregation area is typically above ground, and can have a diameter of . The boundaries of a congregation area are distinct; queens flying a few meters outside the boundaries are mostly ignored by the drones. Congregation areas are typically used year after year, with some spots showing little change over 12 years. Since drones are expelled from a colony during the winter, and new drones are raised each spring, inexperienced drones must find these congregation areas anew. This suggests some environmental cues define a congregation area, although the actual cues are unknown. Congregation areas are typically located above open ground, away from trees or hills, where flight is somewhat protected from the wind (calm winds may be helpful during mating flight). At the same time, many congregation areas do not show such characteristics, such as those located above water or the forest canopy. Some studies have suggested that magnetic orientation could play a role, since drones older than 6 days contain cells in the abdomen that are rich inmagnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula . It is one of the iron oxide, oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetism, ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetization, magnetized to become a ...
.
Congregation areas can be located by attaching a virgin queen (in a cage) to a balloon floating above ground. The person then moves around, taking note of where drones are attracted to the caged queen. Congregation areas are not found closer than from an apiary
An apiary (also known as a bee yard) is a location where Beehive (beekeeping), beehives of honey bees are kept. Apiaries come in many sizes and can be rural or urban depending on the honey production operation. Furthermore, an apiary may refer to ...
, and congregation areas located farther away from apiaries receive more drones. In a congregation area, drones accumulate from as many as 200 colonies, with estimates of up to 25,000 individual drones. This broad mixing of drones is how a virgin queen can ensure she will receive the genetic diversity needed for her colony. By flying to congregation areas further away from her colony, she further increases the probability of out-breeding.
A single drone visits multiple congregation areas during his lifetime, often taking multiple trips per afternoon. A drone's mating flight averages 20–25 minutes, before he must return to the colony to refuel with honey. While at the site, the drones fly around passively, waiting for the arrival of a virgin. When the virgin queen arrives to the congregation area, the drones locate her by visual and olfactory cues. At this point, it is a race to mate with the virgin queen, to be genetically represented in the newly founded colony. The swarming drones, as they actively follow the queen, reportedly resemble a "drone comet", dissolving and reforming as the drones chase the virgin queen. Drones greatly outnumber the quantity of virgin queens produced per season, so even with multiple mating by the queen, very few drones mate successfully (estimated at less than one in 1,000). If needed, a virgin queen can embark on multiple "nuptial flights", to be sure to receive enough semen from enough drones.
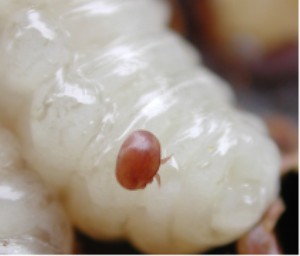
''Varroa destructor''
 ''
''Varroa destructor
''Varroa destructor'', the Varroa mite, is an ectoparasite, external parasitic mite that attacks and feeds on honey bees and is one of the most damaging honey bee pests in the world. A significant mite infestation leads to the death of a honey b ...
'', a parasitic mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as eac ...
, propagates within the brood cell of bees. The ''Varroa'' mite prefers drone brood as it guarantees a longer development period, which is important for its own propagation success. The number of ''Varroa'' mites can be kept in check by removing the capped drone brood and either freezing the brood comb
The brood comb is the beeswax structure of cells where the queen bee lays eggs. It is the part of the beehive where a new brood is raised by the colony. During the summer season, a typical queen may lay 1500-2000 eggs per day, which results in 15 ...
or heating it.
See also
* Western honey bee life cycleReferences
External links
Close-up Video of a Drone bee
Video of drones being expelled from a hive
Drone
{{DEFAULTSORT:Drone (Bee) Beekeeping Insect reproduction Bees